To create a new dBASE database (.dbf), proceed as follows:
| 1. | Choose the ribbon command Mailings | group Database | New database |
| 2. | Select "dBASE" from the list Save as type in the file dialog. |
| 3. | Create your own file name, select a storage location and confirm your entry. |
| 4. | The following dialog box appears: If necessary, change the character set. For further explanations, see below. |
| 5. | Now create the first database field: |
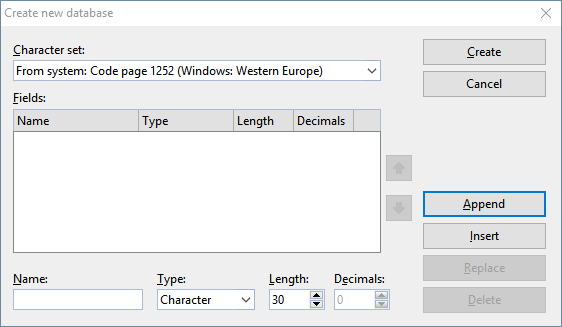 |
| Enter a unique name for the field under Name and select a suitable field type for Type. If necessary, enter the desired Length and the number of decimal places for Dec.. For further explanations, see below. |
| 6. | Once you have made all the specifications for a field, click on Append to add the new field after the last field. |
| If other fields are already defined, you can also click on Insert to insert the new field ahead of the current field. |
| 7. | Repeat steps 5 and 6 for each additional field to be included in the database. You can create a maximum of 254 fields, but the total length of all fields must not exceed 4000 characters. |
| Tip: If you make an error when specifying the field name, field type, etc., and only notice this fact after you have clicked on the Append button, you can go back and correct the error. Click on the relevant field in the list Fields, correct your entries below and click on Replace. You can also delete fields that were created incorrectly by choosing Delete. |
| 8. | When all desired fields have been entered, click on the Create button. |
The database has now been created. You can now close the database or, if necessary, perform further steps on the open database in the database module. For more information, see Using the database module.
With the command Change structure ![]() in the database module, the structure of the created database can be changed retroactively at any time. For more information, see Changing the database structure.
in the database module, the structure of the created database can be changed retroactively at any time. For more information, see Changing the database structure.
Notes on the field type
The option Type in the above dialog box allows you to specify the field type of a field. This determines the type of data to be entered in the field. The following field types are possible (the maximum permissible field length in parentheses):
Field type (length) |
Allowed entries |
Character (1 to 254) |
Character fields allow any type of input. |
Numeric (1 to 19) |
Numeric fields only accept numbers as input. You can set the desired number of decimal places with Decimals. You can even perform calculations with the content of such fields. For more information, see Calculations in the text. |
Date (always 8) |
Date fields are intended for dates. |
Logical (always 1) |
Logical fields are intended for Yes/No entries. The allowed entries are limited to Y for Yes or N for No. |
Memo (always 10) |
Memo fields behave in a different manner to "normal" fields. They accept any type of input and allow you to enter additional notes for a record. Memo fields can only be viewed and edited in the database, but you cannot insert or print these types of fields into documents. Their width is always given as 10, but you can actually enter up to 4000 characters in each memo field. |
Tip: For numbers such as phone numbers, zip codes, etc., select "Character" rather than "Numeric". Numeric fields are of no advantage here – on the contrary: If you try to enter a phone number like "001-555-5555" in a numeric field, Write will not allow the "-" because only numbers are allowed; furthermore, the leading zeros will be automatically removed.
Notes on the supported database formats
The dBASE format is available in different versions. If you use the ribbon command Mailings | New database, you can select the desired variant via the option Character set in the dialog box shown above.
The following variants are supported:
Character set |
Description |
dBASE/DOS |
Databases with DOS character set. |
dBASE/Windows |
Databases with Windows character set: Western Europe or Cyrillic (for the Russian alphabet). |
dBASE/Unicode |
Databases with Unicode character set. This is a variant of the dBASE format developed by Ashampoo that also supports complex character sets (for example, Asian scripts). However, such databases can only be edited with a few programs (apart from Ashampoo Office). |
Note: Most dBASE databases are stored in the format dBASE/DOS. Windows database programs also generally use the DOS format instead of the Windows format.
Note on the database format dBASE/Unicode
In addition to the usual formats dBASE/DOS and dBASE/Windows, Write also supports databases in the format dBASE/Unicode (UTF-8).
This format is a variant of the format dBASE developed by Ashampoo that also supports complex character sets (for example, Asian scripts). This means that you can also store Chinese text in such databases, for example, which is not possible with databases in the formats dBASE/DOS and dBASE/Windows.
However, please note the following when using this format:
Important: Databases in the format dBASE/Unicode (UTF-8) are not dBASE-compatible and can only be edited with a few programs (apart from Ashampoo Office). Thus, you should use this format only if it is important for this database to support the Unicode character set, for example, to enter Asian scripts in it.